19 January 2024
Paula Chan, Senior Portfolio Manager, Fixed Income
Isaac Meng, Portfolio Manager, Fixed Income


In this 2024 outlook, Paula Chan, Senior Portfolio Manager, Fixed Income, and Isaac Meng, Portfolio Manager, Fixed Income, present their baseline views on the key macroeconomic themes that will likely impact China’s bond market in 2024. They also explain why an active China fixed-income strategy should continue generating value for global investors.
Global fixed income markets generally faced another highly volatile year in 2023. Investors maintained a relatively sanguine outlook and were constructive on mainland China assets at the beginning of the period. A view that was based on the country’s reopening and economic recovery theme. Despite this early market optimism, China’s fixed income markets then faced a series of headwinds throughout the year:
Anchored by monetary easing by the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) and rising real yields, driven by low inflation and even deflation, Chinese government bonds (CGBs) enjoyed stable performance throughout 2023. The Bloomberg Aggregate China Total Return (TR) Bond Index gained +2.71% in USD terms over the calendar year 2023.
Chart 1: 2023 market recap – returns in USD
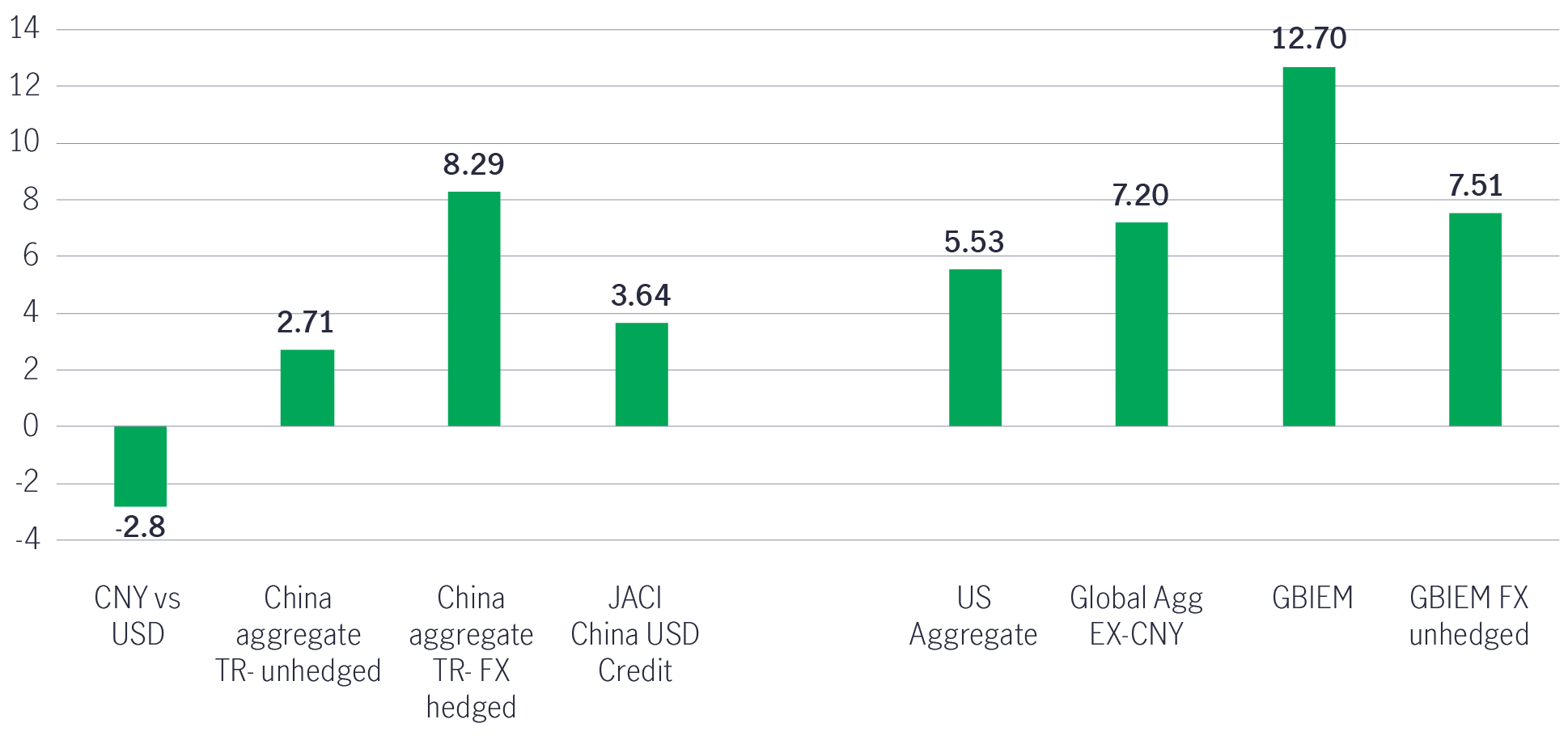
Source: Manulife Investment Management, Bloomberg, as of 31 December 2023. It is not possible to invest directly in an index. Past performance does not guarantee future results. China aggregate TR-unhedged refers to Bloomberg Global Aggregate China TR Index Unhedged, China aggregate TR-FX hedged refers to Bloomberg Global Aggregate China TR Index Hedged, JACI China USD Credit refers to J.P. Morgan China Total Return, US Aggregate refers to Bloomberg US Aggregate Total Return Value Unhedged, Global Agg EX-CNY refers to Bloomberg Global Aggregate Ex-CNY, GBIEM refers to JPMorgan Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets, and GBIEM FX unhedged refers to JPMorgan Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets Unhedged.
Related market moves:
1. Deflation vs interest rates: a call to re-engage policy easing
Mainland China’s policymakers calibrated their 2024 economic planning at the annual Central Economic Work Conference (CEWC) in December 2023. While no major surprises were announced, the CEWC concluded that economic activity had bottomed and the principal of maintaining stability and promoting high-quality growth would be maintained in 2024. Macro policy will also retain an accommodative stance that was observed in 2H23.
Given the weakening recovery momentum of mainland China’s economy, struggling property sector, and emerging signs of debt-deflation pressure across both local government finance and households, we believe there is a strong case for a more aggressive monetary and fiscal stimulus. We have already seen the Ministry of Finance announce a RMB1 trillion Special CGB issuance in the fourth quarter of 2023 to front-load fiscal support to boost growth while additional financing support and regulatory forbearance can be expected to backstop funding needs of leading property developers and local government financing vehicles (LGFVs) to prevent broader contagion across financial markets.
Despite pressure from the Fed’s aggressive rate hikes and the ensuing impact on the CNY against the USD, the PBOC nevertheless cut its one-year medium-term lending facility (MLF) rates by 10 basis points in June and then by a further 15 basis points in August 2023. The cuts confirmed the PBOC’s intention to ease monetary policy to address negative economic developments. Looking ahead, we expect the PBOC to cut policy rates (such as the reverse repo rate and the one-year MLF rate) by 50 basis points, as the window for more aggressive monetary easing will open in early 2024.
While the Fed is likely to begin cutting rates and end quantitative tightening (QT) as inflation approaches its 2% target in the second half of 2024. The market is currently pricing in five to six rate cuts (25 basis points each) in the second half of 2024. Clearly, with this backdrop, the PBOC will have greater freedom to intensify its monetary easing efforts to cushion the property downturn and counter emerging deflationary pressure. The potential re-coupling or convergence of the Fed and PBOC’s respective monetary policies in the direction of further easing will be an important theme for all asset classes going forward. This will also directly impact the attractiveness of Chinese bond yields versus US bond yields and drive the direction of the CNY.
2. Property sector backstop
Despite a series of demand-side mortgage and property easing policies, as well as the “Three Arrows” policies to support financing for leading private property developers that have already been announced since 4Q22, the slump in the property market has continued to intensify.
Property sales have fallen by around 40% vs pre-Covid levels, while the negative spillover to growth and employment has risen with rising systemic financial risks. The contraction of the property sector has also compounded the debt-deflation pressure on households, LGFV and corporate sectors via the wealth channel and physical land market. These risks are well recognized, and consensus is building within authorities to reduce contagion and tail risks. Discussion of “whitelists for property financing” and “quantitative financing targets for banks” are encouraging signals.
In the current environment, we remain cautious, focusing on selective national privately-owned enterprise (POE) developers with leading sales and state-owned enterprise (SOE) developers that potentially benefit from government ownership and explicit government support will likely to continue to be the main beneficiaries as the property sector continues to consolidate, led by this group of SOEs and POE survivors.
Risks to our baseline view
While the above macro themes constitute our constructive 2024 baseline views, the following potential events also need to be closely monitored and can present possible risks to our baseline views.
1. Policies are insufficient – monetary and fiscal policies and property sector policies are too passive and insufficient to counter debt-deflation pressure.
2. Spreading financial risks – policies fail to contain systemic risks, which spread to LGFV and lower-tier SOEs and banks.
3. Geopolitical events – post-Taiwan’s election development in January 2024 and the US presidential election on 5 November 2024. Both events can potentially increase regional tensions and further damage the US-mainland China relationship.
4. US inflation re-acceleration – The Fed could be forced to resume hikes in this scenario, which would be negative for global fixed income.
To summarise, we maintain a bullish outlook for China’s bond markets in 2024.
We forecast that China’s onshore bonds will provide mid-to-high single-digit returns for investors on a CNY basis, with the PBOC likely to intensify easing measures, including cutting repo rates by 50 basis points. At the same time, the government’s fiscal stance will likely turn moderately expansionary.
Neutral to moderate positive on CNY: the Fed is expected to ease by 75-150 basis points in 2024, and mainland China’s more proactive stimulus should provide a constructive backdrop for CNY assets. Global investors’ underweight positioning in CNY assets appears extreme, and we have already seen bond inflows resume in the fourth quarter of 2023. The CNY is expected to remain stable around 7.15 against the USD in early 2024, then moderately appreciate in the second half of 2024 as mainland China’s stimulus gains traction and the Fed begins its easing cycle, leading to the USD index peaking.
For USD-based investors, 2024 looks promising as a year for tactical allocation to CNY bonds. An allocation to CNY bonds on a FX-hedged basis should add +200bp carry to result in a higher single-digit return. On the other hand, a more tactical FX unhedged CNY allocation could benefit from potential moderate CNY appreciation.
CGBs remain an attractive investment for global/emerging-market fixed-income portfolios.
Mainland China’s economic and policy cycles are divergent and often not synchronised with the US and other G3 (the US, Japan, and euro area) economies. Over the years, CGBs have shown low yield beta or often negative correlation to US/global rates. The deep liquidity of both government bonds and CNY FX makes China onshore bonds scalable and ideal for active allocations by global investors.
After another year of slumping property sales, falling prices and cascading POE developer defaults, policy consensus is forming that stabilisation of the property sector is necessary to achieve solid economic recovery and benign relations. The Politburo has highlighted a three-pillar approach to the housing recovery, including urban rehabilitation, public housing, and building strategic facilities. Potentially drawing a playbook of quantitative easing (QE) from G3 policymakers of past decades, mainland China has the resources (including its sovereign/central bank balance sheet) and tools (monetary and fiscal policies) to support the housing market and avoid cascading financial stress. PBOC’s lending facilities, such as pledged supplementary lending (PSL) and local government special bond issuances, have already been engaged to extend trillions. With respect to onshore credit, we have seen little contagion to non-property and LGFV sectors following the volatility in the property sector. At the same time, investor support for high-quality SOE names remains intact.
Chart 2: CNY vs one-year mainland China-US rate difference
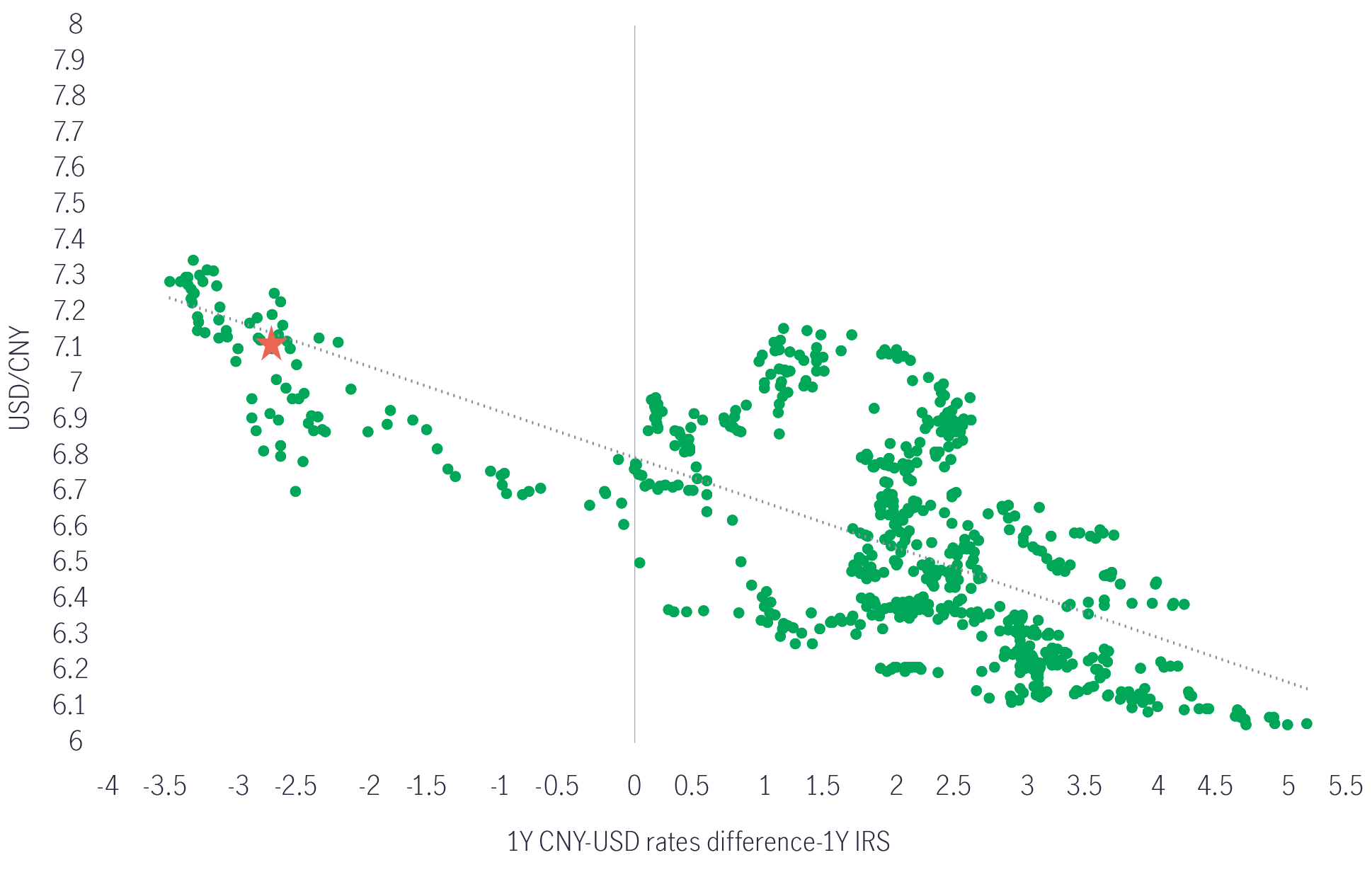
Source: Manulife Investment Management, Bloomberg, as of 31 December 2023. Star refers to the current and end-December data point.
Portfolio positioning
From a positioning perspective, we believe investors can benefit from the following:
After experiencing extreme volatility in global rates, FX and credit in 2023, we believe China’s bond market should continue to offer moderate total returns but with lower volatility, buoyed by expected moderate policy easing, while mainland China’s divergent macro-policy cycle versus other major economies should continue to make China’s bond market attractive for diversification purposes.
1 Debt deflation is an economic theory attributed to economist Irving Fisher. The essence of debt deflation is that when prices and wages fall with the price level, but the nominal size of debts and interest payments are fixed, then borrowers face increasing pressure on the ability to repay. This leads to a leap in loan defaults, which in turn can cause bank insolvencies. The commonly assumed danger of debt deflation is that it can lead to a deflationary spiral, as defaulted debts lead to write-downs by banks and other creditors, which constitute a reduction in the overall volume of money and credit in the economy, which spurs further price and debt deflation in a vicious cycle. Investopedia.
Midyear 2025 global macro outlook: what’s changed and what hasn’t
More forceful-than-expected government policy decisions, particularly by the United States, have swiftly overtaken some of our early 2025 views. Global trade issues and deglobalization have indeed come to the fore, with knock-on effects for many trade-sensitive emerging markets. Elsewhere, capital markets the world over are contending with a big wave of government debt supply, which is driving global bond yields higher.
Greater China Equities: 2H 2025 Outlook
The latest Greater China Equities Outlook highlights how our investment team navigates global uncertainties and invests through the lens of our investment framework via the “4A” positioning: Acceleration, Abroad, Advancement, and Automation.
2025 Outlook Series: Global Healthcare Equities
The Global Healthcare team maintains a sense of measured optimism for the performance of healthcare equities given the underlying key subsector strength in 2025.
Midyear 2025 global macro outlook: what’s changed and what hasn’t
More forceful-than-expected government policy decisions, particularly by the United States, have swiftly overtaken some of our early 2025 views. Global trade issues and deglobalization have indeed come to the fore, with knock-on effects for many trade-sensitive emerging markets. Elsewhere, capital markets the world over are contending with a big wave of government debt supply, which is driving global bond yields higher.
Greater China Equities: 2H 2025 Outlook
The latest Greater China Equities Outlook highlights how our investment team navigates global uncertainties and invests through the lens of our investment framework via the “4A” positioning: Acceleration, Abroad, Advancement, and Automation.
Quick comments on Moody's cut US credit rating
On May 16, credit rating agency Moody's Ratings downgraded the United States' credit rating from Aaa to Aa1. Alex Grassino, Global Chief Economist, together with the Multi-Asset Solutions Team (MAST), Macroeconomic Strategy Team, share their latest views.